CureVac’s (NASDAQ:CVAC) unique dual-variant approach, employing both unmodified and modified mRNA, positions them at the forefront of mRNA-based therapeutics. Their robust financials, underpinned by a robust cash reserve, points towards a stable future. Despite recent dips in earnings and the widened operating loss, analysis suggests that this mirrors a strategic realignment towards long-term growth. Investors should note that CureVac’s current financial snapshot is not a sign of imminent disaster, but rather, confirmatory of its steadfast commitment to groundbreaking research and development (R&D).
The initiation of a first clinical study for their experimental cancer vaccine, CVGBM, marks a promising advance within oncology and could serve as a testament to the potential applications of their second-generation mRNA technology. CureVac has managed to defy logistics and storage challenges, a common hurdle for mRNA-based vaccines, by ensuring stability at regular fridge temperatures, which amplifies its attractiveness to regions with inconsistent electricity supplies.
Financials
CureVac’s fiscal outlook appears robust, with its cash reserves rising impressively to a total of €617.5 million at the end of Q1 2023 from a previous €495.8 million at the conclusion of 2022. This impressive leap of €121.7 million is predominantly attributable to a substantial €219.8 million acquired during the follow-on offering in February. With this ample cash reserve, the company demonstrates financial stability and resilience, enabling them to cover operational costs and invest in R&D.
curevac.com/en/investor-relations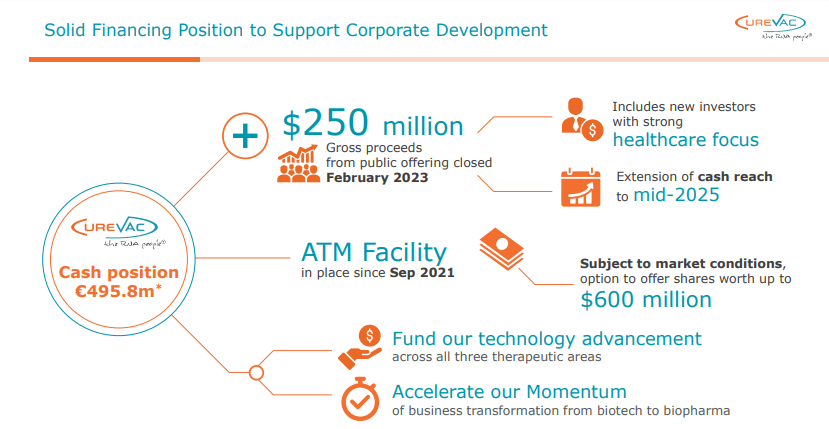
On the other hand, the Q1 2023 earnings, announced to be €7.1 million, represent a significant plunge of 71% from Q1 2022’s €24.4 million, which could be interpreted as a hurdle. Nonetheless, this decline does not indicate impending disaster for the company. The key reason for the reduced revenue points to a realignment of business strategy rather than a defect in the corporate structure or the market’s reaction to the company’s products. This reduction hints at a shift from the high-earning partnership with GSK (GSK), now amounting to €6.5 million from a previous hefty €23.7 million in Q1 of last year.
Although the operating loss for Q1 2023 has climbed to €60.4 million, a considerable leap from €15.3 million in Q1 2022, the situation needs to be fully understood. This includes consideration for the reduced sales expenses, mainly due to decreased write-offs of raw materials. Furthermore, this reflects CureVac’s strategic focus on increased investment in R&D , especially in the potentially ground-breaking sectors of infectious diseases and cancer. The growth in R&D expenditure calls to mind the one-off net gain and the €32.5 million GSK compensation received in 2022, a phenomenon unlikely to recur and hence widening the operating loss. Even at this operating loss, the company can still fund development for another 10 quarters at the current burn rate, providing significant runway before additional funding may be needed.
Simultaneously, CureVac’s Q1 2023 net financial performance was €3.0 million, a substantial climb from the previous €0.1 million in 2022, which can mainly be ascribed to the interest income accrued from cash investments. This showcases CureVac’s financial savvy and its capability to profit substantially from such investments. On the contrary, a pre-tax deficit of €57.4 million compared to €15.2 million in the initial quarter of 2022 is remarkable, but it attests to a commitment to fostering long-term growth, particularly vibrant in the sphere of ground-breaking R&D.
Products
Renowned for its inventive endeavors in the medical field, CureVac is committed to unlocking the therapeutic potential of messenger RNA, commonly referred to as mRNA. Naturally occurring within cells, mRNA serves as a biological messenger, transmitting genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes to facilitate protein synthesis. Building upon this process, CureVac has masterminded a technique that involves the injection of artificial mRNA molecules within cells, which in turn stimulates the production of beneficial proteins like antigens, antibodies, and enzymes, culminating in a curative reaction.
To maximize productivity, CureVac employs two distinctive varieties of mRNA: unmodified and chemically altered or modified types. Unmodified mRNA mirrors the natural constitution of mRNA molecules within the cell, whereas the modified variant undergoes unique chemical changes to increase stability, boost immunogenicity, and improve translation efficacy. Depending on the desired outcome and the specific target tissue, CureVac utilizes diverse delivery techniques, such as lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), protamine compounds, or direct injection protocols.
The efficacy of CureVac’s innovations lies within the successful transportation of mRNA molecules to cells via the most suitable distribution mechanisms. Once these molecules infiltrate the cells, they disengage from their delivery route and migrate to the ribosomes. Here, the mRNA undergoes a translation process to synthesize proteins. Consequently, these proteins exhibit their therapeutic powers by stimulating immune responses, resolving genetic irregularities, combating harmful pathogens, or even impeding disease progression. Thus, CureVac’s unique strategy capitalizes on cellular processes naturally to evoke healing responses to a myriad of ailments.
curevac.com/en/investor-relations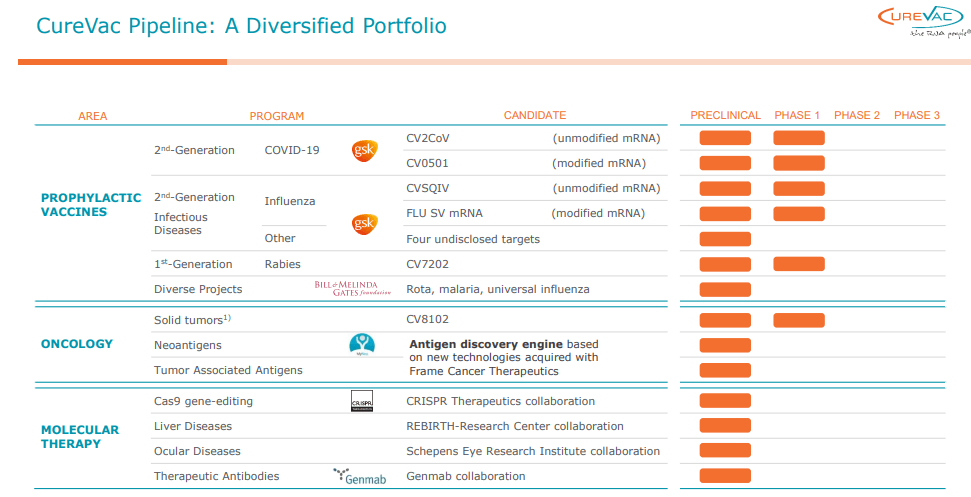
CVGBM Clinical Trial: Advancing Cancer Vaccine Innovation
CureVac has announced a significant step forward in its trial advancements. This key development features the first administration of a patient dosage involving its experimental cancer vaccine, CVGBM, as part of an initial clinical trial. Underpinned by CureVac’s exclusive second-generation mRNA technology, CVGBM is systemically formulated using a single mRNA that encodes eight epitopes derived from globally recognized tumor-linked antigens, significant markers in glioblastoma. The projection for the first set of data to be released falls in the latter part of 2024.
The launch of this primary clinical test for CVGBM heralds an imperative milestone in CureVac’s journey to developing a cancer vaccine. The trial aims to validate the potential of CureVac’s advanced second-generation mRNA technology in the field of oncology. The outcomes of the trial will provide crucial evidence regarding the ability of CureVac’s mRNA solution to stimulate potent immune responses against tumors. These findings are predicted to further solidify the company’s strategic position and broaden its oncology drug portfolio.
This trial, designed as an open-label study, is engineered to assess the safety and patient tolerance of CVGBM in newly diagnosed patients with MGMT-unmethylated glioblastoma or astrocytoma that exhibit the molecular characteristics of glioblastoma following surgical excision. The proposed trial design includes the administration of CVGBM as a solitary therapy post-operative and post-radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy. The trial follows a bifurcated structure, comprised of a dose escalation phase (Part A) and a dose expansion section (Part B). In the current Part A phase, patients are slated to receive seven intramuscular injections of CVGBM, with increasing doses ranging from 12 to 100 µg on defined days. Assuming no disease advancement, post-day 71 vaccinations with CVGBM will be continued every six weeks for up to a year from the first CVGBM vaccination or until disease progression or severe toxicity occurs.
Mechanistic Risks
CureVac’s pioneering approach of using mRNA as a stimulant for the production of therapeutic proteins harbors immense potential. Yet for the success of these scientific endeavors, it is essential to navigate certain plausible hurdles.
The first challenge lies in accurately delivering mRNA molecules to their targeted cells. CureVac has devised various methods for delivery, including LNPs, protamine formulations, and procedures involving direct injection. However, it’s essential to consistently achieve efficient and targeted delivery to eliminate unwanted off-target effects and maintain therapeutic efficacy.
Another potential barrier is finding the right balance between the stability and translational efficiency of mRNA molecules. Efforts have been made to reinforce the stability of mRNA molecules by modifying them, but care must be taken to prevent these modifications from disrupting the overall functionality and translation of these molecules.
Additionally, one must also take into account the immunogenic potential of mRNA-based drugs. Despite modified mRNA being designed to tamp down on immunogenic responses, it’s still of utmost importance to closely monitor immune reactions. Appropriate strategies need to be in place to mitigate any possible adverse effects, which if left unchecked, could hamper the effectiveness of therapeutic proteins and raise safety concerns.
Consideration must also be given to the optimal dosage level and duration of treatment. It’s crucial to establish a dosage that will trigger the desired therapeutic effect without causing toxicity or long-term complications. Furthermore, to maintain a therapeutic response over the required duration, the sustained and controlled release of therapeutic proteins must be assured.
Competitors
The distinctive characteristics of CureVac’s mRNA technology offer a unique edge over competitors in the biopharmaceutical sector. While Pfizer-BioNTech (PFE) and Moderna (MRNA) also employ mRNA technology, these companies primarily use modified mRNA. CureVac’s platform offers both unmodified and modified mRNA, giving them a broader therapy portfolio and providing more diverse therapy options.
One specific competitor to CureVac is Moderna. Their mRNA technology, although similar in principle, exclusively uses modified mRNA molecules. Modified mRNA promotes longer protein production and greater translational efficiency but may induce more significant adverse events. The potential side effects of modified mRNA, such as inflammatory reactions, are typically less prominent with the use of unmodified mRNA, an aspect that underscores CureVac’s advantage in terms of safety profile.
Similar to Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine employs modified mRNA. However, it demands exceptionally low storage temperatures – around -70 degrees Celsius. In contrast, CureVac’s vaccines are stable at regular fridge temperature. This makes distribution and storage considerably easier and cheaper, particularly in regions with inconsistent electricity supply or a lack of ultra-cold storage facilities.
Conclusion
Although certain conventional metrics might imply a sub-optimal performance, CureVac presents a powerfully compelling investment opportunity, particularly for investors seeking a long-term foothold in the biopharmaceutical sphere.
A closer examination of the balance sheet confirms CureVac’s solid financial position. The significant growth in cash reserves serves as a clear testament to the company’s strong fundraising capabilities and responsible financial management. This robust fiscal resilience provides sufficient cushioning for operational expenses while consistently supporting their ambitious R&D endeavors.
Further solidifying the bullish outlook on CureVac, the recent initiation of the clinical trial for CVGBM is a testimony to their relentless scientific advancement and dogged determination in the oncology realm. Their inventive mRNA technology doesn’t just promise therapeutic breakthroughs but holds the potential to revolutionize the dynamics of the biotech industry.
Read the full article here