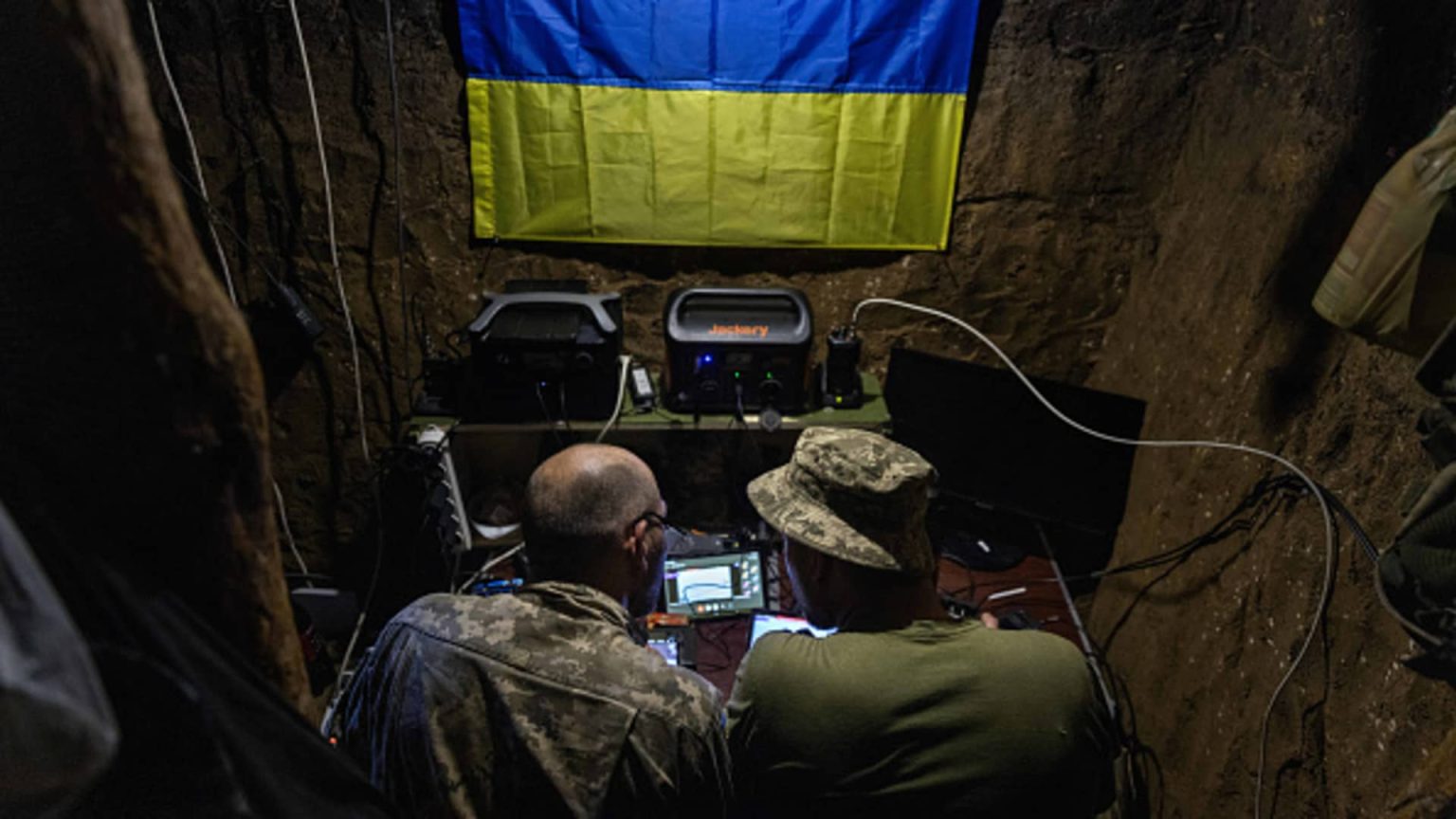
Ukraine’s counteroffensive has been more sluggish than many expected and military analysts warn that the window of opportunity for breaking through Russian defenses — and making territorial gains — could close soon.
Kyiv’s counteroffensive was launched in June after months of preparation, but its progress has disappointed some onlookers who hoped for a faster regaining of Russian-occupied territory in the south and east of the country.
While Ukraine planned its counteroffensive over the winter — and waited for more military hardware from its international allies — Russian forces were heavily fortifying their positions along a 900-kilometer (559-mile) front line stretching from the Kharkiv-Luhansk border in the northeast of Ukraine, toward Kherson in the southwest.
Military analysts note that Ukraine now faces successive lines of Russian defenses that are, in some cases, 30 kilometers deep and consisting of minefields, anti-tank obstacles and extensive networks of trenches and bunkers that are covered by Russian drones, artillery and helicopters.
Small window of opportunity
One of the biggest problems for Ukraine is that the timeframe for breaking through Russia’s defenses is limited, with only a few summer months left in which to make serious gains.
For Michael Clarke, a defense analyst and former director-general of the Royal United Services Institute (RUSI) think tank, there’s a risk that the first phase of the counteroffensive, designed to probe Russia’s defenses, takes too long.
“It was always intended to be a two-stage offensive, with a sort of probing first stage to try to identify weaknesses in the Russian frontline, followed by a second stage where they put their big forces into it. And we’re still on the first stage which has lasted longer than they expected,” he told CNBC Wednesday.
“If this first phase lasts too long, they leave themselves insufficient time before the weather changes, before the second phase starts,” he said. Although he believed it to be an unlikely scenario, Clarke noted that time pressures could prompt Ukraine to deploy military units destined for use in the second phase of the counteroffensive sooner than planned — something he said Russia is hoping for.
“The danger then is that they will not be able to use the bulk of their forces in sufficient mass to make a difference … to create a real punch when they decide to really start,” he added. “I’m not pessimistic about this offensive but the risks that it may not work are increasing as the days tick on.”
One of the most pressing time constraints is the inevitable change of weather, with Ukraine’s infamous muddy season in the fall set to make the offensive far more challenging and at times — with unpassable roads and fields — practically impossible.
Konrad Muzyka, a military intelligence specialist and president of Rochan Consulting, said “the weather has always been the factor” for Kyiv.
“I think that the Ukrainians expected the counteroffensive to gather sufficient momentum to allow them to continue to push south at a much faster rate. Unfortunately, it didn’t happen,” he told CNBC Wednesday.
“I think it’s fair to say that Ukrainians have up to three months now before they will run out of artillery munitions and they will run out of barrels for their guns, and three months until the terrain will again become very muddy.”
Lost momentum
The scale of the challenge facing Ukraine became apparent when early momentum in the counteroffensive, which saw Ukraine reclaim a handful of occupied villages in the south, seemingly petered out.
But Kyiv says its forces are conducting counteroffensive actions in at least three areas and are operating against a backdrop of increased Russian offensive operations. Ukraine’s defense ministry claims that its forces have liberated around 210 square kilometers (81 square miles) of occupied territory since June. Meanwhile, the attritional nature of the counteroffensive is becoming increasingly apparent.
“Ukrainians tend to say that ‘we captured a trench’ or ‘we moved 500 meters forward’ and so on and so forth but essentially what we are seeing is a very hard-fought battle on the Ukrainian side,” Muzyka said.
“This reminds me of the battles we have seen since mid-last year, when one side is trying to push the front line, and the other side is very well dug in and is trying to prevent any breakthroughs,” he added.
Muzyka said Ukraine’s attacks on Russian positions are ongoing and have been reasonably successful so far, but any advances are likely to be slow. In addition, expectations of any major breakthrough in the counteroffensive were low among Ukrainian soldiers he had spoken to on the ground.
“This will have to be a grinding attritional fight after the next two or three months,” he noted.
“The objective is to continue to push forward and liberate trench by trench in a slow manner. The use of armored vehicles is very limited because the density of Russian ATGMs [anti-tank guided missile systems] and artillery is so, so high, that it’s still risky to use combined armored formations.”
“The Ukrainians will just have to inch forward and continue to strike the Russian rear hoping that the Russian ability to sustain the forces in the north will be sufficiently degraded to allow for the increased tempo of ground attacks on the Ukrainian side,” Muzyka noted. “To what extent this will be successful, I don’t know.”
Ukraine and allies defend progress
Ukraine is the first to admit that its troops are operating in what one defense official described this week as “extremely difficult conditions.” They have conceded that the counteroffensive is going more slowly than expected and is not having the swift results of similar actions last year, which saw Kyiv’s forces retake a swathe of Kharkiv in northeast Ukraine and Kherson in the south.
Yuriy Sak, an advisor to Ukraine’s defense ministry, defended the military’s progress and repeated calls for fighter jets from its allies — the supply of which continues to elude Kyiv.
“If you consider that we are conducting these offensive operations along the 900-kilometer long front then you are possibly going to conclude that this is going pretty well,” Sak told CNBC Wednesday.
“If you take into account the millions of mines that have been laid, the length of the trenches and fortified defense lines and that we’re doing this without the air power, and Russians continue to have air supremacy, then the progress is steady and positive.”
Ukraine’s allies continue to insist they will support Ukraine for as long as it takes. Asked on Monday whether he considered the counteroffensive a failure so far, U.S. General Mark Milley, chair of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, said “it is far from a failure. I think that it’s way too early to make that kind of call,” Reuters reported.
“I think there’s a lot of fighting left to go and I’ll stay with what we said before: This is going to be long. It’s going be hard. It’s going to be bloody.”
Read the full article here